Visual Cliff

Gibson and R.D. Walk developed the visual cliff test to use with human infants and animals. Earlier research had revealed that infants will respond to various depth cues even before they are able to crawl.
THE VISUAL CLIFF AND FEAR OF HEIGHTS. Fear of falling is one of the most fundamental and biologically-adaptive emotions humans and terrestrial animals have. The Visual Cliff. Child Psychology Lab 310L. Reference: Gibson, E. (1960) The Visual Cliff. Scientific American, 202, 80-92.
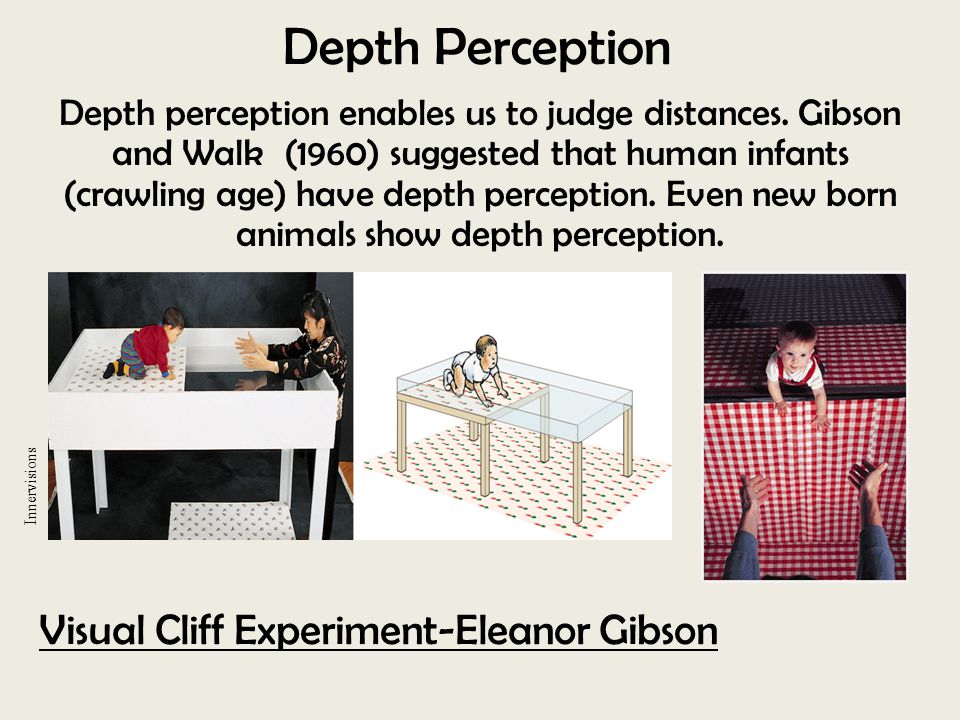
Depth cues allow people to detect depth in a visual scene. These can include both such as relative size and overlap, or binocular cues such as retinal disparity. Gibson and Walk were interested in whether or not an infant's ability to perceive depth is a learned behavior or if it was, as they suspected, innate. Gibson and Walk described their visual cliff apparatus as a large sheet of heavy Plexiglass supported a foot or more off the floor. El Arte De La Negociacion Pdf Donald Trump.
On one side of the glass, a high-contrast patterned fabric is pressed up against the underside to make the glass appear solid. The same material is laid on the floor below the glass, creating the visual illusion of a cliff. This allowed researchers to test infant perception while still ensuring the safety of their young subjects. It was also assumed that infants who still lacked depth perception would crawl happily to their caregivers without even noticing the apparent drop.
Gibson and walk concluded that the ability to perceive depth emerges sometime around the age that an infant begins to crawl. The fear of heights, they suggested, is something learned later in infancy as gain experience with bumps, scrapes, and falls. Understanding the Visual Cliff Initially, believed that perception of the visual cliff was a matter of physical and visual maturity. Babies could see the difference by the age of 8 months, while younger infants with less developed depth perception could not see the cliff. Because 6-month-old children could be enticed to wiggle across the visual edge, while 10-month-old children refused to cross the threshold, it was assumed that the younger children had not yet developed depth perception while the older children had.