Diff Between Jar War And Ear Files Java
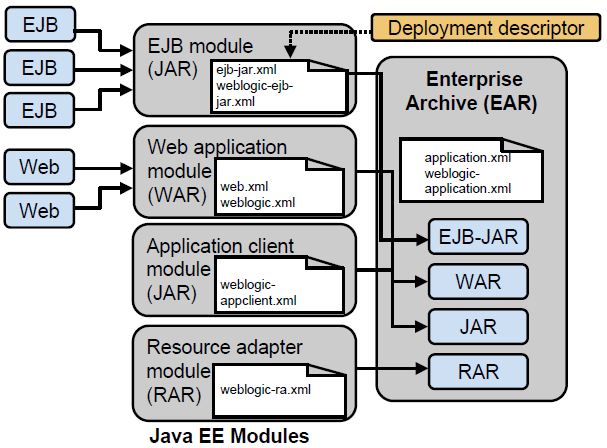
EAR is an EEnterprise Aapplication archive and may contain ejb JAR files, WAR files, and RAR (connector) files. They may also contain third-party libraries - but you have to know how to manipulate the Java extension facilities (e.g. Gamecube Pokemon Xd Der Dunkel Sturm Download Youtube. MANIFEST.MF Class-Path directive) to make that work well. In this tutorial we see what is Jar, War and Ear files in Java enterprise development, and also see what is the difference and usage of these files.
Answered by Jey on 2005-05-08 11:23:41: In J2EE application modules are packaged as EAR, JAR and WAR based on their functionality JAR: EJB modules which contains enterprise java beans class files and EJB deployment descriptor are packed as JAR files with.jar extenstion WAR Web modules which contains Servlet class files,JSP FIles,supporting files, GIF and HTML files are packaged as JAR file with.war( web achive) extension EAR All above files(.jar and.war) are packaged as JAR file with.ear ( enterprise archive) extension and deployed into Application Server. In J2EE application modules are packaged as EAR, JAR and WAR based on their functionality JAR: EJB modules which contains enterprise java beans class files and EJB deployment descriptor are packed as JAR files with.jar extenstion WAR Web modules which contains Servlet class files,JSP FIles,supporting files, GIF and HTML files are packaged as JAR file with.war( web achive) extension EAR All above files(.jar and.war) are packaged as JAR file with.ear ( enterprise archive) extension and deployed into Application Server. Hai,There are no structural differences between the files; they are all archived using zip-jar compression. However, they are intended for different purposes.--Jar files (files with a.jar extension) are intended to hold generic libraries of Java classes, resources, auxiliary files, etc.
--War files (files with a.war extension) are intended to contain complete Web applications. In this context, a Web application is defined as a single group of files, classes, resources,. Introduction To Biotechnology Thieman Ebook Library. jar files that can be packaged and accessed as one servlet context.
--Ear files (files with a.ear extension) are intended to contain complete enterprise applications. In this context, an enterprise application is defined as a collection of.jar files, resources, classes, and multiple Web applications. Each type of file (.jar,.war,.ear) is processed uniquely by application servers, servlet containers, EJB containers, etc. EAR is an EEnterprise Aapplication archive and may contain ejb JAR files, WAR files, and RAR (connector) files.
They may also contain third-party libraries - but you have to know how to manipulate the Java extension facilities (e.g. MANIFEST.MF Class-Path directive) to make that work well. WAR is an Web Aapplication archive and contains JSPs, 'normal' HTTP served files (HTML, images, etc.), servlets, tag libraries, and such. JAR is the 'normal' Java Aapplication archive, but in this context it usually contains EJBs instead of code libraries or runnable (e.g. From outside an application container) applications. In J2EE application modules are packaged as EAR, JAR and WAR based on their functionality JAR: EJB modules which contains enterprise java beans class files and EJB deployment descriptor are packed as JAR files with.jar extension WAR: Web modules which contains Servlet class files, JSP FIles, supporting files, GIF and HTML files are packaged as JAR file with.war(web archive) extension EAR: All above files(.jar and.war) are packaged as JAR file with.ear (enterprise archive) extension and deployed into Application Server.